The world of business isn't just about companies selling to individual consumers. There's a whole other realm where businesses interact and conduct transactions with each other – the fascinating world of B2B, or business-to-business.
What exactly is B2B?
Imagine a manufacturer purchasing raw materials from a supplier, a restaurant hiring a cleaning service, or a software company partnering with a marketing agency. These are all examples of B2B transactions. In essence, B2B refers to the exchange of goods, services, or information between businesses. It's the backbone of complex supply chains and the driving force behind countless industries.
Why is B2B important?
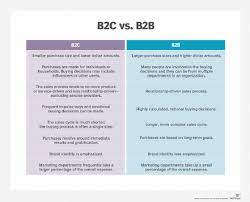
B2B plays a crucial role in the global economy. It accounts for a significant portion of total trade and creates millions of jobs worldwide. B2B transactions often involve larger volumes and higher values compared to B2C (business-to-consumer) interactions, making it a major contributor to economic growth.
What are the key characteristics of B2B?
Here are some of the unique aspects of B2B commerce:
- Longer sales cycles: B2B decisions often involve complex evaluations, negotiations, and approvals, leading to longer sales cycles compared to B2C.
- Rational purchasing decisions: B2B buyers are driven by logic and ROI (return on investment) rather than emotions or impulse purchases.
- Relationship-based approach: Building strong relationships with key decision-makers and understanding their specific needs is crucial for success in B2B.
- Complex pricing models: B2B pricing can be more intricate than B2C, with discounts, bulk agreements, and customized rates often playing a role.
- Emphasis on technology: Digital tools and platforms are increasingly used in B2B marketing, sales, and communication.
Different types of B2B businesses:
The B2B landscape is diverse, encompassing a wide range of businesses:
- Manufacturers: Companies that produce goods used by other businesses in their production processes.
- Wholesalers: Businesses that buy large quantities of goods from manufacturers and resell them to other businesses.
- Distributors: Companies that act as intermediaries between manufacturers and retailers or other businesses.
- Service providers: Businesses that offer professional services to other businesses, such as marketing agencies, consulting firms, and IT service providers.
- Technology companies: Businesses that develop and sell software, hardware, and other technology solutions to other businesses.
The future of B2B:
The B2B landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing customer expectations, and globalization. Some key trends shaping the future of B2B include:
- Increased use of e-commerce platforms: B2B buyers are increasingly turning to online platforms to research, compare, and purchase goods and services.
- Growing emphasis on data and analytics: B2B businesses are using data and analytics to gain deeper insights into customer behavior, optimize operations, and personalize their offerings.
- Focus on building stronger customer relationships: Building trust and long-term partnerships with customers will be crucial for success in an increasingly competitive B2B environment.
B2B is essential for anyone interested in the world of business. It's a complex and dynamic field with immense potential, offering exciting opportunities for entrepreneurs, marketers, and business professionals alike. So, whether you're a seasoned business veteran or just starting your journey, take some time to explore the fascinating world of B2B – you might just discover the next big business opportunity!






0 Comments